What is Cassandra Back

- Cassandra is a ideal database used for social network. It combines Dynamo of Amazon with BitTable of Google, which is based on Column Family(列簇).
- Official Suggestion: The Apache Cassandra database is the right choice when you need scalability(可擴展性) and high availability without compromising performance.
- Some characteristics:
- Dynamo:
- Symmetric(對稱的) P2P framework
- Without special node(solving the problem of SPOF(單點失效))
- Distributed Management based on Gossip
- Store data with distributed hash tables.
- pluggable partition(可插拔分區)
- pluggable topologies(可插拔拓撲)
- pluggable store strategies(可插拔存放策略)
- Configurable(eventual consistency)
- Symmetric(對稱的) P2P framework
- BigTable:
- Column Family Data Model
- configurable, 2-levels maps, super column family
- SSTable
- Append-only commit log
- Memtable(buffer and sort)
- Unmodifiable SSTable files
- Integrated Hadoop
- Column Family Data Model
- Dynamo:
Data Model
- Column: the minimum components of a data, and it's composed of Name, Value, and Timestamp.
- Notice: name and value should be byte[], which a string of any length.
{
"name": "email",
"value": "[email protected]",
"timestamp": 1455517240
}
- SuperColumn: the name is same as Column, while the value is a set of columns. In additionally, they don't have timestamps.
{
"name": "addresses",
"value": {
"street": { "name": "street", "value": "xxx xxx xxx Road", "timestamp": 1455517515 },
"city": { "name": "city", "value": "Foshan", "timestamp": 1455517515 },
"zip": { "name": "zip", "value": "528031", "timestamp": 1455517515 }
}
}
- Both SuperColumn Family and Column Family describe a set of SuperColumn and Column.
- Sorting:
- Notice: in Cassandra, data is sorted by Column name by default.
- Configurable:
- Set
CompareWithAttribute (Column Family) - Set CompareSubColumnsWith (SuperColumn Family)
- Set
- Value for configuration:
- BytesType
- UTF8Type
- LexicalUUIDType
- TimeUUIDType
- AsciiType
- Column name
Partition Strategies
- In Cassandra, Token is the key point for partitions, and there is a unique token for each node, describing the range of data in which. All the tokens will be stored as a ring(Cassandra Ring), and use hash value to calculate.
- There are 3 strategies for partitions in Cassandra:
- Random Partitioner:
- Token will be a BitInteger(0 ~ 2127), mapped with hash. (In Cassandra, it will take a 128 bits MD5 absolute value, which contains a sign bit)
- In a in-extreme(極端的) situation, it can map 2127 + 1 nodes.
- Notice: it's not supported that searching data with key in this strategic.
- Order Preserving Partitioner(ordered):
- Token will be a string.
- It depends on the key to certain which nodes to be chosen
- Notice: without Initial Token, system will take a 16 bits random strings which contain numbers and alphabets as the token.
- Collating Order Preserving Partitioner(ordered):
- Token will be a byte.
- Configurable sorting in different languages(en_US by default)
- Random Partitioner:
- Partition strategies and Token(including Initial Token) can be set in the file storage-conf.xml.
Bloom Filter
- Bloom Filter is a random data structure, saving huge space by sacrificing precision. (This structure cannot be applied to applications which are sensitive to accuracy.)
- In Cassandra, each key-value pair will use one byte to complete Bloom Filter.
- Read more details in Wikipedia
Storage Strategies
- In Cassandra, data will be stored in the local file system of each node with 3 strategic to copy data:
- Simple Strategy(RackUnaware Strategy): copies will be saved in the next several nodes behind this node.
- OldNetwork Topology Strategy(RackAware Strategy): one copy will be saved in a different node, while other N - 2 copies will be saved in other machines in the same node.
- Network Topology Strategy: M copies will be saved in different nodes, while N - M - 1 copies will be saved in different machines of the same node.
- Storage mechanisms:
- Commit Log: Cassandra will log records when writing data like HBase. After logging, data will be written into memtable and flushed into the SSTable, which is read-only once written into. (In Cassandra, there is no random write)
- Memtable: when data has reached the size of a block, it will be flushed into the disk, and stored as SSTable.
- SSTable: it's read-only and one CF will be corresponding with several SSTable. Bloom Filter will be used to justify which SSTable the key belongs to.
- Compaction used in Cassandra:
- Garbage Collect: delete the data which is really signed.
- Merge SSTable in the same CF.
- Generate a Merkle Tree.
- Compaction used in Cassandra:
- Read more details in IBM documents
Sniffing(嗅探)
- Sniffing is mainly used to calculate the distance between different host to tell Cassandra what the topology looks like. There are 3 strategies to configure:
- org.apache.cassandra.locator.SimpleSnitch: logical distance(the difference between Cassandra Ring)
- org.apache.cassandra.locator.RackInferringSnitch: the distance depends on rack(the third 8 bits in IP) and data center(the second 8 bits in IP)
- org.apache.cassandra.locator.PropertyFileSnitch: the distance depends on rack and data center, which are both configured in the configuration file, cassandra-topology.properties.
Consistency
- Eventual Consistency is used in Cassandra. Users can choose different level of consistency to use.
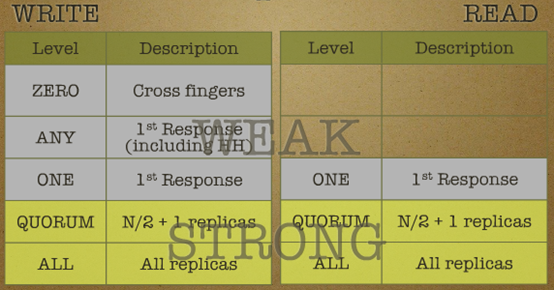
- Notice: the level of consistency depends on the number of copies instead of the number of nodes.
Quorum NRW
- N: means the number of copies once(In generally, N > 3 in a distributed system to ensure fault-tolerance)
- R: means the minimum of nodes which is successful to read once
- W: means the minimum of nodes which is successful to write once
- In Quorum, consistency will be strong when W + R > N, but availability will be low.
In Quorum, consistency will be weak when W + R <= N, but availability will be high. (This will be used generally when eventual consistency is guaranteed)
In Cassandra, there are 4 methodologies to ensure eventual consistency:
- Anti-Entropy(逆熵): the mothod used to check consistency called Merkle Tree.
- Read Repair: repair in the case that finding it's not consistent when reading data from key A and all the copies of key A.
- ONE: return a recent copy immediately, and repair in the background. (The first data you read will not be the latest one)
- QUORUM: return a copy when there is no problems after checking more than half of all copies, and check remaining copies and repair if necessary in the background.
- ALL: return a copy when there is no problems after checking all.
- Hinted Handoff(提示提交): write to a relay node when the target is offline, and the relay node will wait for the target to complete writing.
- Distributed Delete: Cassandra will sign a hint to the object which is deleted by other nodes, and this object will be collected when doing Garbage Collect at the fixed time.