Introduction Back
1. Importance of project management
- A 1995 Standish Group study (CHAOS) found that only 16.2% of IT projects were successful in meeting scope, time, and cost goals; over 31% of IT projects were canceled before completion.
- A PricewaterhouseCoopers study found that overall half of all projects fail and only 2.5% of corporations consistently meet their targets for scope, time, and cost goals for all types of project.
- Advantages of using formal project management:
- Better control of financial, physical, and human resources
- Improved customer relations
- Shorter development times
- Lower costs
- Higher quality and increased reliability
- Higher profit margins(利益邊際)
- Improved productivity
- Better internal coordination
- Higher worker morale(士氣)
2. Definitons
- Projects:
- projects are unique.
- operations(業務) is work done to sustain(支撐) the business.
- end when:
- their objectives have been reached
- the project has been terminated.
- can be large or small, and take a long or short time to complete.
- Stakeholders: the people involved in of affected by project activities.
- the project sponsor
- the project manager
- the project team
- support staff
- customers
- users
- suppliers
- opponents(競爭對手) to the project
3. The triple constraint
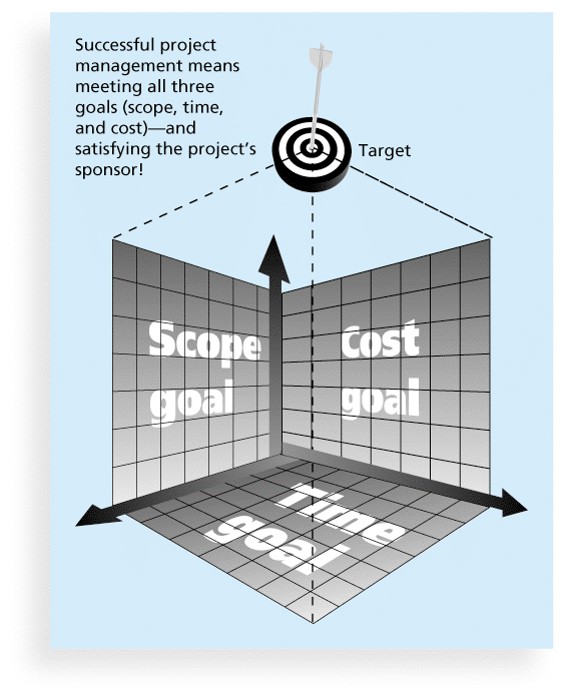
- there is a triple constraint of project management:
- Scope:
- What work will be done as part of the project?
- What unique product, service or result does the customer or sponsor expect from the project?
- How will the scope verified(證實)?
- Cost:
- What should it cost to complete the project?
- What is the project's budget?
- How will costs be tracked?
- Who can authorize changes to the budget?
- Time:
- How long it take to complete the project?
- What is the project's schedule?
- How will the team track actual schedule performance?
- Who can approve changes to the schedule?
- Scope:
- quadruple constraint includes quality as well.
4. The frameswork of project integration management
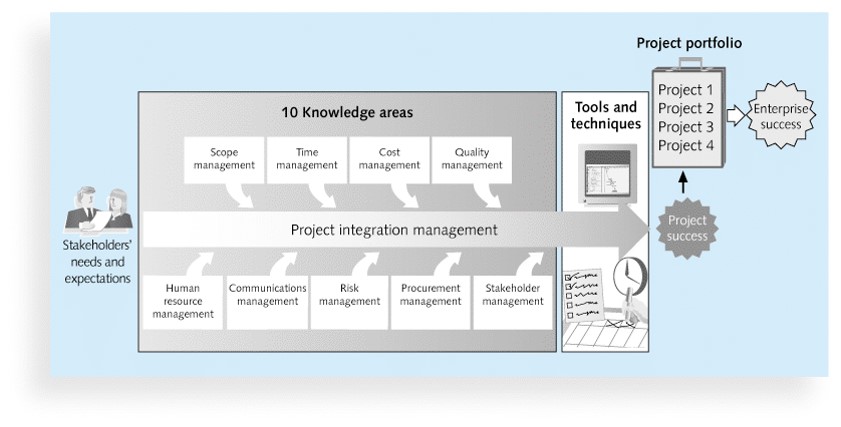
- Knowledge Areas(KA):
- Stakeholders(有權益關係者) Management: Helps you identify and manage relationship with people who can impact(衝擊) or who get impacted by the project.
- Procurement(採購) Management: If at all some part of yor project work is to be done by an expert seller, this KA has all the know-how(專業知識) of how to deal with it.
- Risk Management: There will be plenty of threats as well as opportunities. Identify them. Analyze them. Prepare for them. When they do happen, address and control them!
- Communication Management: Helps you keep all stakeholders in the know. Distribute right information to the right people at the right time.
- Human Resources Management: People, People, People! A crucial(至關重要的) element of success for any project. And, most challenging for the Project Manager. Why? Because dealing with people needs great deal of interpersonal(人際) skills!
- Integration Management(the start point): integrating processes covers from Initiating to Closing of the project or phase.
- Scope Management: Helps you understand stakeholders' expectations out of the project. (very crucial)
- Time Management: You will be able to identify project activities, identify dependencies, estimate ther resource and durations are estimated, and create project schedure right here!
- Cost Management: Address all type of costs - direct & indirect costs, related to quality, resources, risks and procurement.
- Quality Management: Figure out what is needed to ensure that project produces PSR(product/service/result) that is in line with stakeholders' expectations - not more, not less!
5. Factors to help projects succeed
- User involvement
- Executive support(行政支持)
- Clear business objectives
- Emotional maturity(情感成熟度)
- Optimizing scope(樂觀領域)
- Agile process
- Project mangement expertice(專業知識)
- Skilled resources
- Execution
- Tools and infrastructure(基礎設施)
6. Q&A
- What is the difference between projects and operations?
answer: Projects are temporary endeavors whereas an organization's operations are ongoing in nature.
- Which project management knowledge areas is an overarching function that affects and is affected by the different knowledge areas?
answer: Project Integration Management
- Is checklist a tool used in quality management?
answer: Yes.
- Which of the following tools can best hep in efficient communication management?
- Kick-off meetings
- Requests for quotes
- Impact matrices
- Fast tracking
answer: Kick-off meetings.
- What is the difference between project management and portfolio management?
answer: Project management addresses specific short-term goals whereas portfolio management focuses on long-term goals.
- Martha works as a project manager at a bank. Due to certain changes in external factors, Martha needs to make a few alterations in the tactical goals of her project. In such a scenario, which of the following will best help Martha cope with the change?
- Negotiation
- Project environment knowledge
- Motivation
- Soft skills
answer: Project environment knowledge.
- Which is the organizational group responsible for coordinating the project management function throughout an organization?
answer: Project Management Office.
- Which of the following provides certification as a Project Management Professional?
- PMS
- PMI
- PMC
- PMP
answer: PMI.
- Which of the following refers to a set of principles that guides decision making based on personal values of what is considered right and wrong?
- Ethics
- Civics
- Laws
- Politics
answer: Ethics.