Information Technology Context Back
1. Systems view
- Project managers need to use systems thinking: to take a holistic(整體的) view of carrying out projects within the context of the organization.
- a systems approach includes:
- Systems philosophy
- Systems analysis
- Systems management
2. Three Sphere(領域) Model of Systems Management
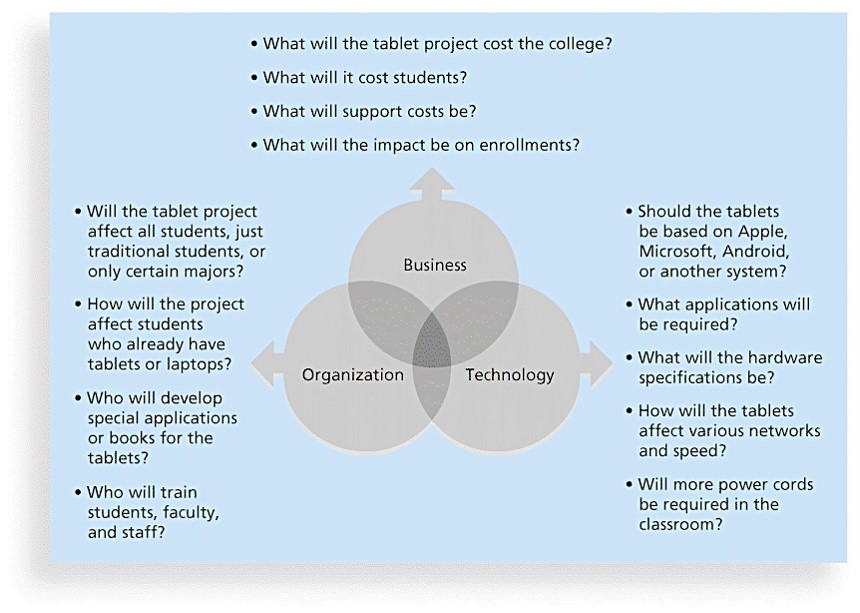
- Organizations:
- Structural frame: Roles and responsibilities, coordination and control. (Organizational charts help describe the frame)
- Human resources frame: Providing harmony between needs of the organization and needs of people.
- Political frame: Coalitions(並集) composed of varied individuals and interest groups. Conflicts and power are key issues.
- symbolic frame: Symbols and meanings related to events. Culture, language, traditions and image are all parts of this frame.
3. Organizational Structures

- Functional: functional managers -> CEO
- Project: program managers -> CEO
- Matrix: personnel -> two or more bosses (between functional and project structures)
4. Organiazational Culture
- a set of shared assumptions, values and behaviors that characterize the functioning of an organiaztion.
- characteristics of organizational culture (bold means it's more important):
- Member identify
- Risk tolerance
- Group emphasis
- Reward criteria
- People focus
- Conflict tolerance
- Unit integration
- Means-ends orientation(導向)
- Control
- Open-systems focus
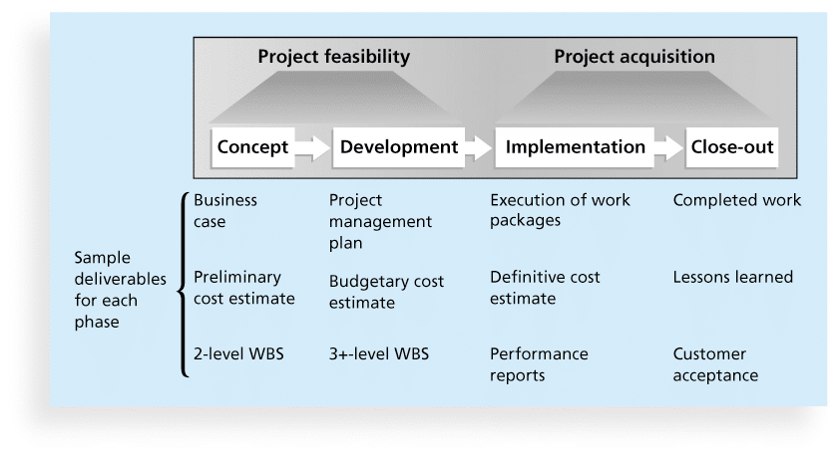
5. Project Life Cycle
- a project life cycle: a collection of project phases. (from the projects' start point to the end point)
- phases of a traditional project life cycle.
- a Systems Development Life Cycle(ADLC) is a framework for describing the phases involved in developing and maintaining information systems. A system development project can follow:
- Predictive life cycle: the scope of the project can be clearly articulated(清楚說明的) and the schedule and cost can be predicted.
- Waterfall Model: has well-defined, linear stages of systems development and support.
- Spiral Model: shows that software is developed using an iterative(迭代) or spiral(螺旋) approach rather than a linear approach.
- Incremental Build Model: provides for progressive(漸進的) development of operational software.
- Prototyping(原型) Model: used for developing prototypes to clarify user requirements.
- Rapid Application Development(RAD) Model: used to produce systems quickly without sacrificing(犧牲) quality.
- Adaptive software development life cycle: requirements cannot be clearly expressed, projects are mission driven and component based, using time-based cycles to meet target dates.
- Agile Development Model
- Predictive life cycle: the scope of the project can be clearly articulated(清楚說明的) and the schedule and cost can be predicted.
6. Definitives
- Globalization: software has been completed by people all around the world in many companies.
- Outsourcing(外包): an organization acquires goods and/or sources from an outside source.
- Offshoring(離岸外包): to describe outsourcing from another countries.
- Virtual teams: a group of individuals working across time and space using communiation technologies.
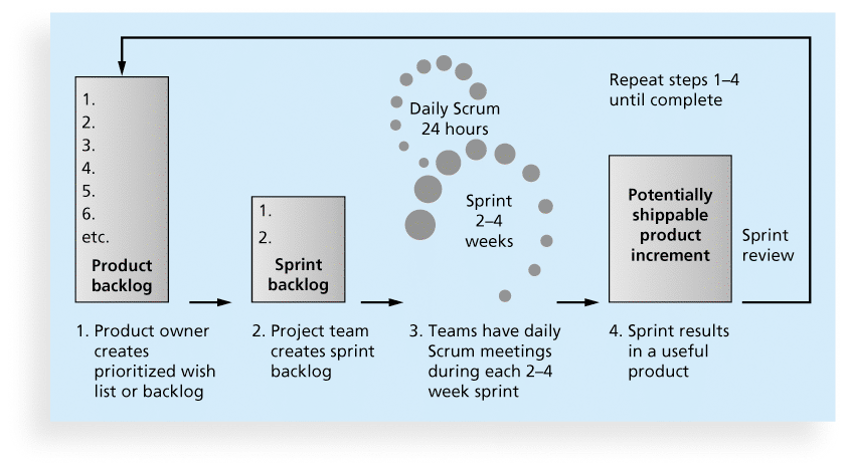
7. Scrum Framework
- Scrum Framework is a leading agile development method.
8. Q&A
- In what organizational structure, program managers, rather than functional managers or vice presidents, report to the CEO. Their staffs have a variety of skills needed to complete all required tasks within their programs.
answer: Project.
- Which of the following is true of a matrix organizational structure?
- In a matrix organizational structure, employees are organized into departments according to their skills, and there is little interaction between employees from different departments.
- Project managers in matrix organizations have staff from only a single functional area working on their projects.
- In a strong matrix organizational structure, the project manager controls the project budget and has moderate to high authority.
- A matrix organizational structure is hierarchical, but instead of functional managers reporting to the CEO, program managers report to the CEO.
answer: In a strong matrix organizational structure, the project manager controls the project budget and has moderate to high authority.
- Which characteristic of organizational culture describes the degree to which management's decisions take into account the effect of outcomes on people within the organization?
answer: people focus.
- What refers to the degree to employees identify with the organization as a whole, rather than with their types of job or profession?
answer: Member identity.
- What refers to the degree to which departments within an organization are encouraged to coordinate with each other?
answer: Not group emphasis, but unit integration.
- What refers to the degree to which the organization monitors and responds to changes in the external environment?
answer: Open-systems focus.
- The first two traditional project phases (concept and development) focus on planning, and are often referred to as what?
answer: project feasibility.
- In what phase, the project team creates a definitive or very accurate cost estimate, delivers the required work, and provides performance reports to stakeholders?
answer: implementation.
- Which of the following is a disadvantage of virtual teams as compared to traditional teams?
- Increased costs for office space and support
- Limited flexibility in team working hours
- Reduced opportunities for informal transfer of information
- Reduced dependence on technology and processes for accomplishing work
answer: Reduced opportunities for informal transfer of information.