Thread Back
- Thread(線程)指一個程序中的執行片段,且擁有併發執行的特性.
- 線程間通信可通過共享全局變量來實現
同步&互斥
- 同步: 指事件處理存在一定的協作順序,而這個順序的改變將會導致結果的差錯. (Semaphore)
- 互斥: 指多個進程將要讀取同一區域(關鍵區)的數據時,將只能允許一個進程進入. (Mutex)
Ways to create a thread
- Inherit from the calss Thread (java.lang.Thread)
class MyThread extends Thread
{
//Attributes
MyThread()
{
//Constructor
}
@SuppressWarnings("deprecation")
public void run()
{
//What you want this thread to do
}
}
implements Runnable interface
with this
class MyThread implements Runnable { Thread t; MyThread() { t = new Thread(this); t.start(); } //Implements public void run() { //What you want this thread to do } }with unnamed inner class
Thread MyThread = new Thread( new Runnable() { public void run() { //What you want this thread to do } });
some methods of Threads
- join()
t.join(); //Wait for this thread to die
- yield()
t.yield(); //Causes the currently executing thread object to temporarily pause
//and allow other threads to execute.
- setPriority(int newPriority)
t.setPriorty(MAX_PRIORITY); //Changes the priority of this thread to a max one
/* java.lang.Thread
* public static final int MAX_PRIORITY 10
* public static final int MIN_PRIORITY 1
* public static final int NORM_PRIORITY 5
*/
When sharing same datas
/* do with shared datas */
public synchronized void transfer()
{
//synchronized label ensures that this thread won't be schedule out when running this method.
}
States of a Thread
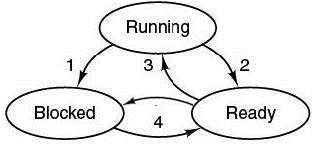
- Process blocks for input
- Scheduler picks another process
- Scheduler picks this process
- Input becomes available
- Blocked State
Thread.sleep(100); //Blocked State (do not release lock)
@Deprecated
Thread.suspend();
wait(); //Blocked State (release lock and need other threads to call notify() or notifyall())
- Run State
Thread t = new MyThread() //Initialize
t.start(); //Run State
//Ready State: Waiting CPU to call it
- Ready State