Project Quality Management Back
- ISO defines quality as "the degree to which a set of inherent characteristics fulfills requirements".
- Other experts define as:
- Conformance(一致) to requirements
- Fitness to use
1. Processes
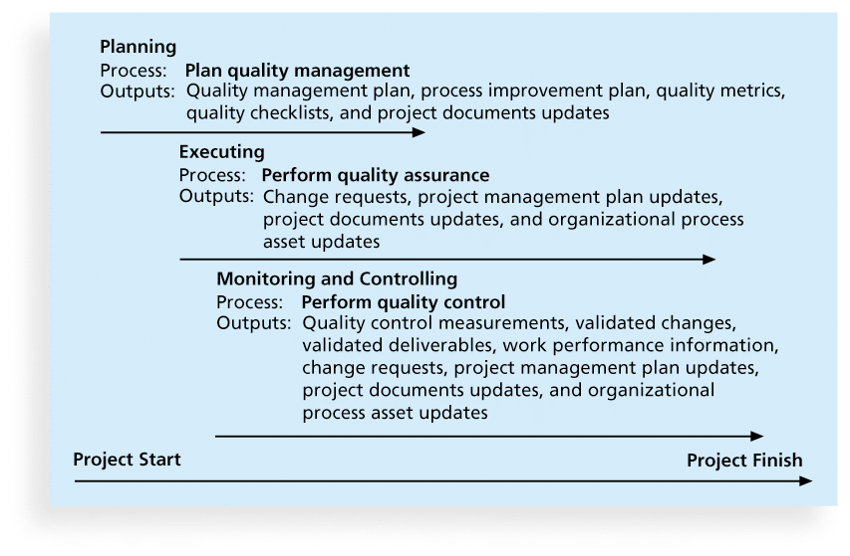
- Planning quality management
- Scope Aspects of IT Projects:
- Functionality
- Features
- System outputs
- Performance
- Reliability
- Maintainability
- Project managers are ultimately(最終) responsible for quality management on their projects.
- Scope Aspects of IT Projects:
- Performing quality assurance
- Quality assurance includes all the activities related to satisfying the relevant quality standards for a project.
- Benchmarking(基準) generates ideas for quality improvements by comparing specific project practices or product characteristics to those of other projects or products within or outside the performing organization.
- A quality audit is a structured review of specific quality management activities that help identify lessons learned that could improve performance on current or future projects.
- Performing quality control
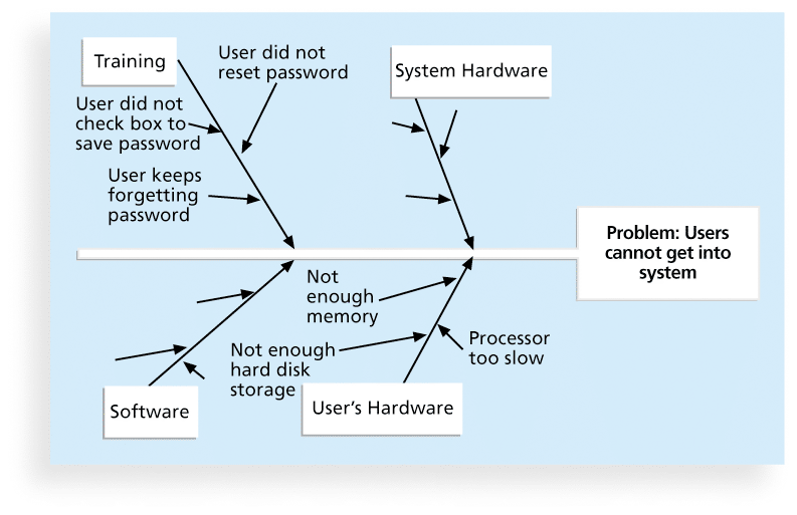
2. Cause-and-Effect Diagrams
- Cause-and-effect diagrams trace complaints about quality problems back to the responsible production operations. (Also called fishbone diagrams or Ishikawa diagrams)
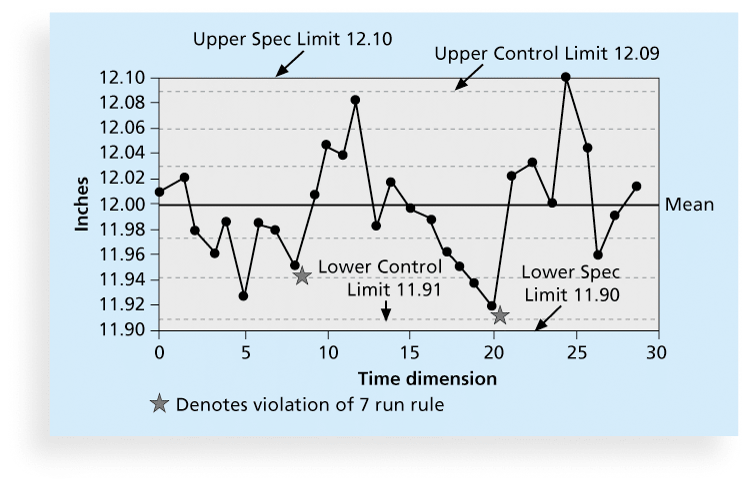
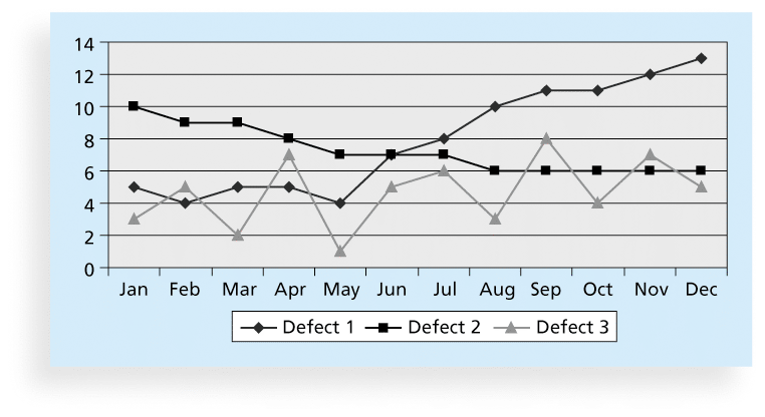
3. Quality Control Charts
- A control chart is a graphic display of data that illustrates the results of a process over time.
- The main purpose of using control charts is to prevent defects(缺陷) rather than to detect or reject them.
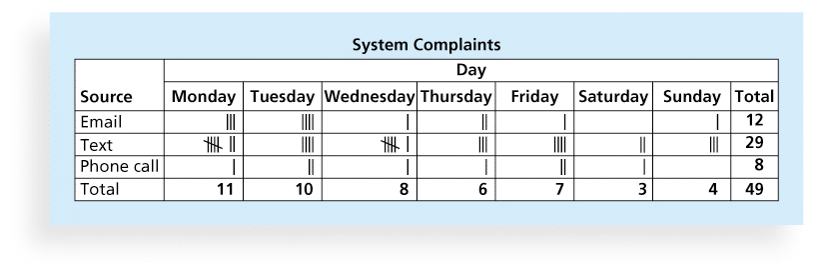
4. Checksheet
- A checksheet is used to collect and analyze data. (Also called tally sheet or checklist)
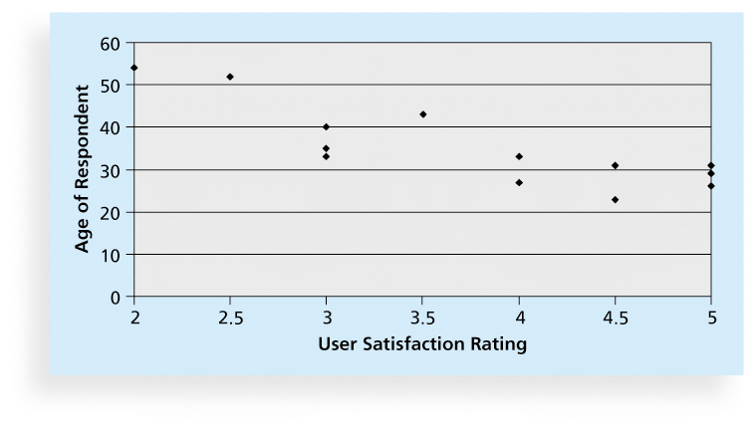
5. Scatter Diagrams
- A scatter diagram helps to show if there is a relationship between two variables.
- The closer data points are to a diagonal line(对角线), the more closely the two variables are related.
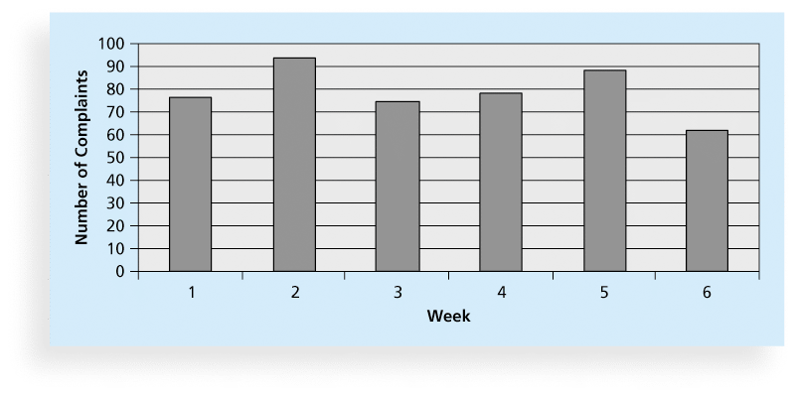
6. Histograms
- A histogram is a bar graph of a distribution of variables.
- Each bar represents an attribute or characteristic of a problem or situation, and the height of the bar represents its frequency.
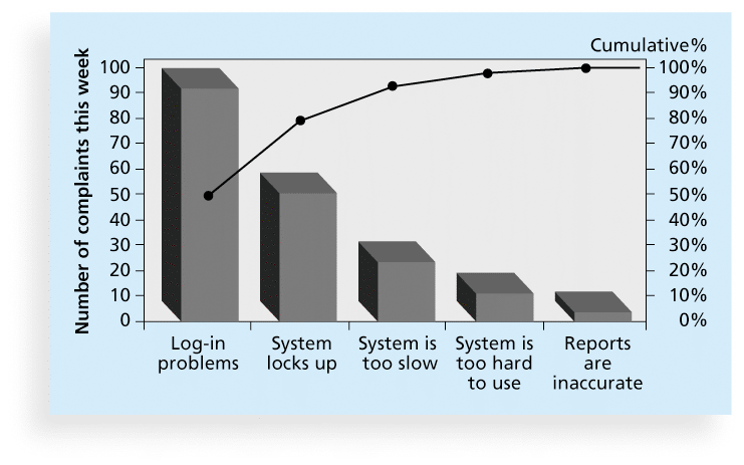
7. Pareto Charts
- A Pareto chart is a histogram that can help you identify and prioritize problem areas.
- Pareto analysis is also called the 80-20 rule, meaning that 80 percent of problems are often due to 20 percent of the causes.
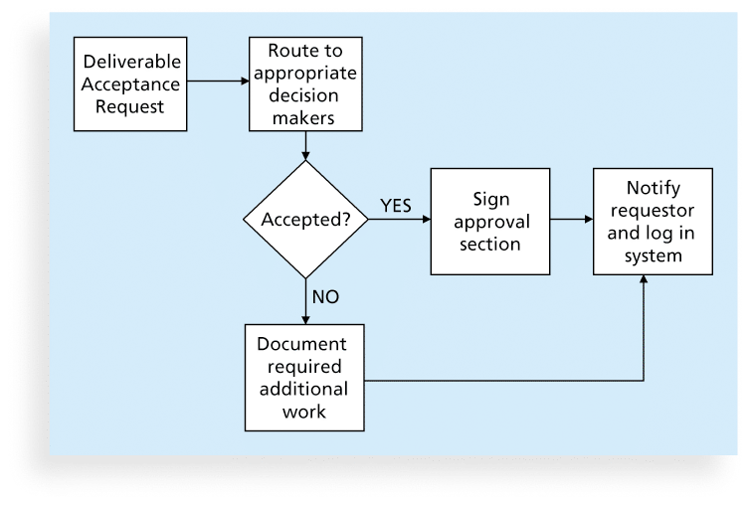
8. Flowcharts
- Flowcharts are graphic displays of the logic and flow of processes that help you analyze how problems occur and how processes can be improved.
9. Run Charts
- A run chart displays the history and pattern of variation of a process over time.
10. Testing
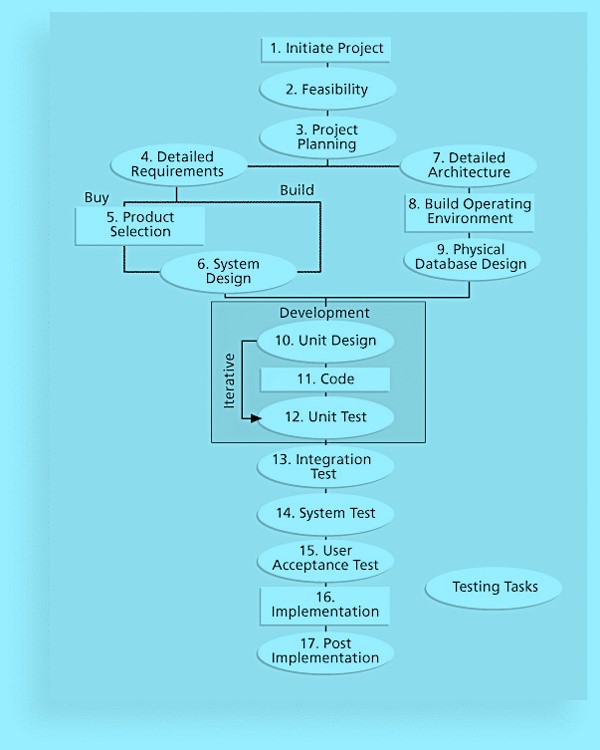
- Unit testing tests each individual component (often a program) to ensure it is as defect-free as possible.
- Integration testing occurs between unit and system testing to test functionally grouped components.
- System testing tests the entire system as one entity.
- User acceptance testing is an independent test performed by end users prior to accepting the delivered system.
- Watts S. Humphrey, a renowned expert on software quality, defines a software defect as anything that must be changed before delivery of the program.
11. Maturity Models
- Maturity models are frameworks for helping organizations improve their processes and systems.
- The Software Quality Function Deployment Model focuses on defining user requirements and planning software projects.
- The Software Engineering Institute's Capability Maturity Model Integration is a process improvement approach that provides organizations with the essential elements of effective processes.
12. CMMI Levels
- CMMI Levels is a formal standard to identify the quality of a software companies.
- 0: Incomplete
- 1: Performed
- 2: Maged
- 3: Defined (government projects baseline)
- 4: Quantitatively Managed
- 5: Optimizing
13. Q&A
- What is a standard of measurement in quality management?
- milestone
- merge
- metric
- matrix
answer: metric.
- What is the degree to which a system performs its intended function?
- Reliability
- Maintainability
- Validity
- Functionality
answer: Functionality.
- What are the system's special characteristics that appeal to users.
- Features
- Yields
- Outputs
- Metrics
answer: Features.
- What generates ideas for quality improvements by comparing specific project practices or product characteristics to those of other projects or products within or outside the performing organization?
- Prototyping
- Mind mapping
- Systems thinking
- Benchmarking
answer: Benchmarking.
- What refers to action taken to bring rejected items into compliance with product requirements or specifications or other stakeholder expectations?
- A process adjustment
- An acceptance decision
- Rework
- Validation
answer: Rework.
- What correct(s) or prevent(s) further quality problems based on quality control measurements?
- Process adjustments
- Acceptance decisions
- Rework
- Decomposition
answer: Process adjustments.
- What is a graphic display of data that illustrates the results of a process over time?
- statistical sampling chart
- Six Sigma chart
- Pareto chart
- control chart
answer: control chart.
- What help users to identify the vital few contributors that account for most quality problems in a system?
- Gantt charts
- Control charts
- Pareto charts
- Tracking Gantt charts
answer: Pareto charts.
- What involves choosing part of a population of interest for inspection?
- Statistical sampling
- System testing
- Conformance
- Fitness for use
answer: Statistical sampling.
- Six Sigma's target for perfection is the achievement of no more than how many defects, errors, or mistakes per million opportunities?
- 1.34
- 34
- 3.4
- 13.4
answer: 3.4.
- Important tools used in which phase of the DMAIC process include a project charter, a description of customer requirements, process maps, and Voice of the Customer(VOC) data?
- define
- analyze
- measure
- improve
answer: define
- What is a bell-shaped curve that is symmetrical regarding the average value of the population (the data being analyzed)?
- skewed distribution
- bimodal distribution
- normal distribution
- degenerate distribution
answer: normal distribution
- What is a measure of quality control equal to 1 fault in 1 million opportunities problems.
- ISO 9000
- seven run rule
- six 9s of quality rule
- Six Sigma rule
answer: six 9s of quality rule
- Which of the following is one of Deming‘s 14 Points for Management?
- An organization should increase dependence on inspection to achieve quality.
- Minimize total cost by working with multiple suppliers rather than a single supplier.
- Award business based on price tag alone rather than on other considerations.
- Eliminate the annual rating or merit system.
answer: Eliminate the annual rating or merit system.
- One of Juran's ten steps to quality improvement states that:
- an organization should minimize top management involvement in the achievement of individual employee goals.
- an organization should build awareness of the need and opportunity for improvement.
- an organization should entrust improvement to individual employees rather than appointing teams or facilitators.
- an organization should avoid "keeping score" in order to achieve an overall atmosphere of quality improvement.
answer: an organization should build awareness of the need and opportunity for improvement.
- Who wrote Quality Is Free in 1979 and is best known for suggesting that organizations strive for zero defects?
- Juran
- Crosby
- Ishikawa
- Deming
answer: Crosby.
- What is the cost of evaluating processes and their outputs to ensure that a project is error-free or within an acceptable error range?
- Prevention cost
- Internal failure cost
- Appraisal cost
- External failure cost
answer: Appraisal cost.
- What is a cost that relates to all errors not detected and not corrected before delivery to the customer?
- Prevention cost
- Internal failure cost
- Appraisal cost
- External failure cost
answer: External failure cost.
- What helps integrate traditionally separate organizational functions, set process improvement goals and priorities, provide guidance for quality processes, and provide a point of reference for appraising current processes?
- SQFD
- OPM3
- MTBI
- CMMI
answer: CMMI.