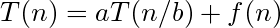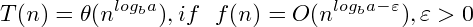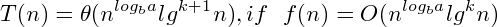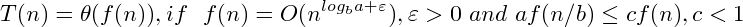How to analyse an algorithm Back
1. Overview
Main thoughts of designing algorithms:
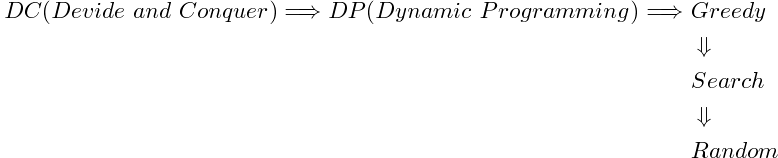
Sometimes, the performance of an algorithm matters so much, when the size of a problem n is so big.
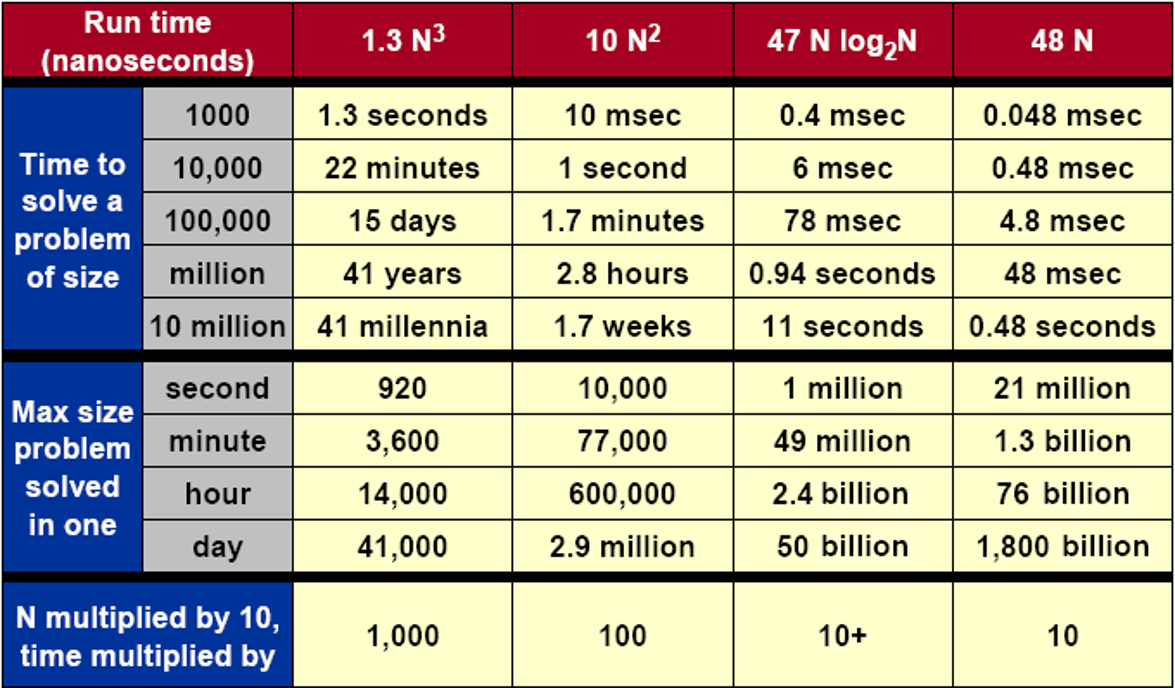
But it's not always true for high performance, when an algorithm depends on what is more important like the following items:
- modularity(模塊性)
- correctness(正確性)
- maintainability(可維護性)
- functionality(功能性)
- robustness(健壯性)
- user-friendliness(用戶友好性)
- programmer time(編程效率)
- simplicity(簡潔度)
- extensibility(可擴展性)
- reliability(可靠度)
There are three kinds of analysis:
- Worst-case(考慮該類問題的最優解, 關注最壞情況下的最好情況)
- Average-case
- Best-case(虛假的)
There are three notations of time
- θ (drop low-order terms, and ignore leading constants)
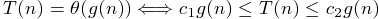

- Ω
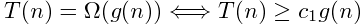
- O
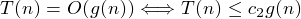
2. Recursive Algorithm
Substitution: 猜想 (通常通過畫Recursive Tree來給出猜想) 並證明
- guess
verify
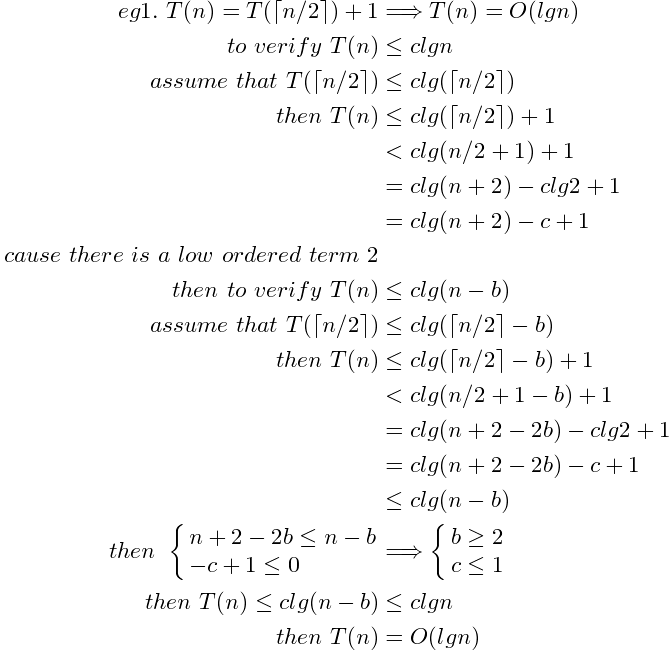
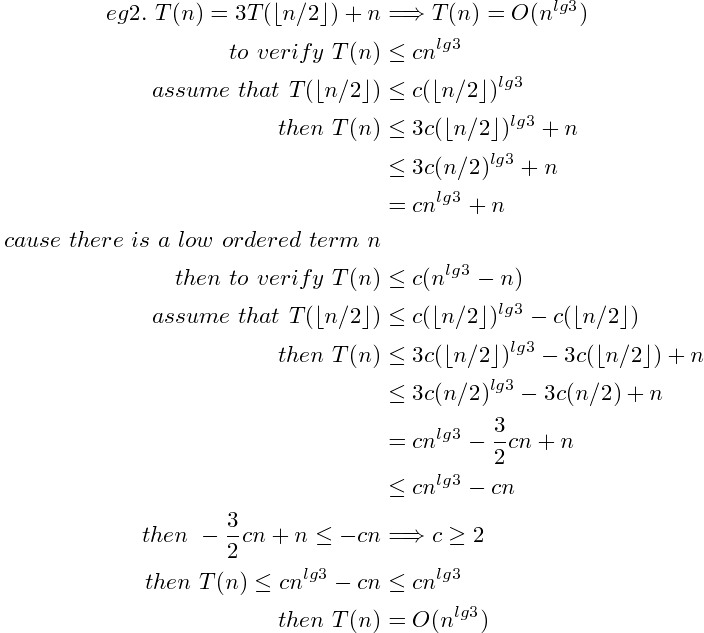
- solve
- Recursive Tree: 通過畫出遞歸樹來求解開銷
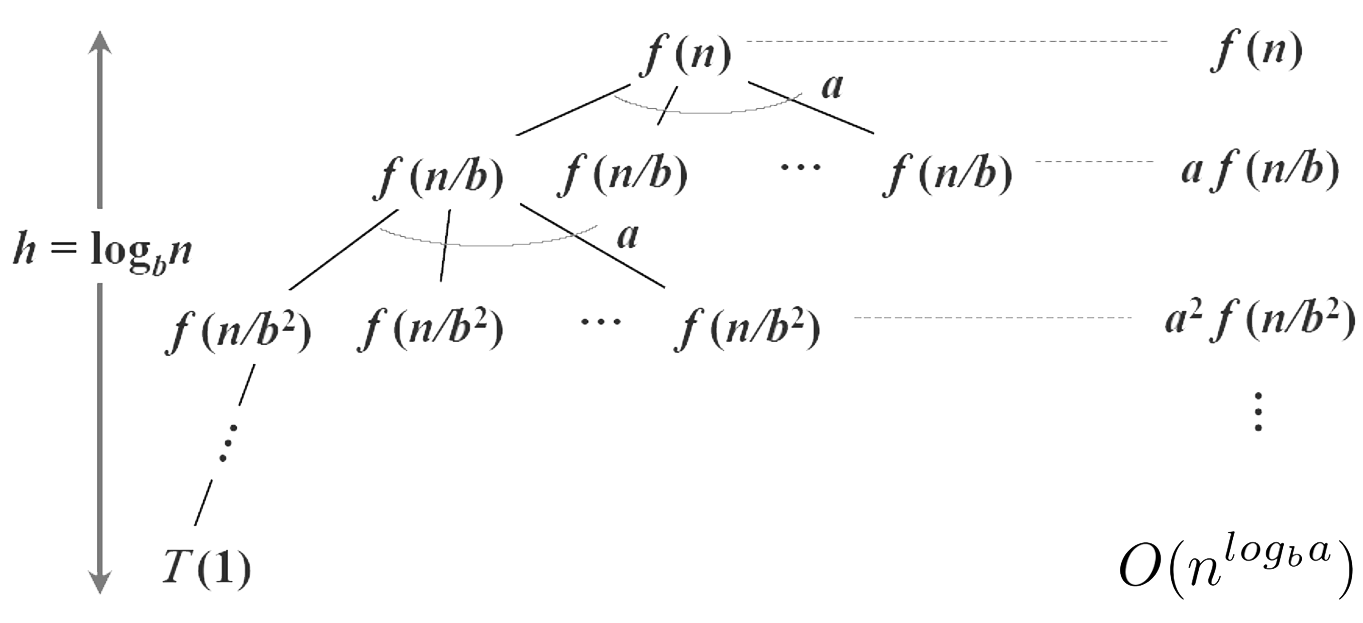
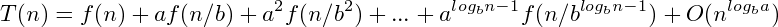
Master: