Crash Course of PHP Back
1. Embedding PHP in HTML
- PHP tags:
- XML Style:
<?php echo '<p>Order processed.</p>'; ?>
- Short Style:
<? echo '<p>Order processed.</p>'; ?>
- SCRIPT Style:
<script language='php'> echo '<p>Order processed.</p>'; </script>
- ASP Style:
<% echo '<p>Order processed.</p>'; %>
<html>
<head>
<title>Bob's Auto Parts - Order Results</title>
</head>
<body>
<h1>Bob's Auto Parts</h1>
<?php
echo '<p>Order processed.</p>';
?>
</body>
</html>
2. PHP Statements
2.1 Whitespace
<?php echo 'hello ' . 'world' ?>
<?php echo 'hello ' . 'world' ?>
<?php
echo ‘<p>Order processed.</p>'; // Start printing order
?>
<?php
echo ‘<p>Order processed.</p>';
?>
<?php
echo ‘<p>Order processed.</p>'; /* Start printing order */
?>
2.3 Function
<?php
data('H:i, jS F');
?>
2.4 Variables
- short style: requires the register_globals configuration setting be turned on with the reson of security issue.(off by default)
- medium style: solve the security issue.(recommended)
- $_POST: the form was submitted via the POST method.
- $_GET: the form was submitted via GET method.
- $_REQUEST: th for was submitted via either POST or GET method.
- long style: used on old server.
$var
$_POST['var']
$HTTP_POST_VARS['var']
<?php
$tireqty = $_POST['tireqty'];
$oilqty = $_POST['oilqty'];
$sparkqty = $_POST['sparkqty'];
?>
2.5 String Concatenation(字符串連接)
- A period(.) is the string concatenation operator, which adds astrings together.
echo('Hello' . ' world');
3. Variable Types
3.1 Data Type
- Integer
- Float
- String
- Boolean
- Array
- Object
- NULL: variables that have not been given a value.
- resources: represents external resources (such as database connections)
3.2 Type Strength
- PHP is called weakly typed, or dynamically typed language.
3.3 Variable Variables
- To enable you to change the name of a variable dynamically.
$varname = 'tireqty';
$$varname = 5;
4. Declaring and Using Constants
define('TIREPRICE', 100);
define('OILPRICE', 10);
phpinfo() provides a list of PHP's predefined variables and constants, among other useful information.
5. Variable Scope
- 6 basic scope rules in PHP:
- Built-in superglobal variables are visible everywhere within a script.
- Constants, once declared, are always visible globally; that is, they can be used inside and outside functions.
- Global variables declared in a script are visible throughout that script, but not inside functions.
- Variables inside functions that are declared as global refer to the global variables of the same name.
- Variables created inside functions and declared as static are invisible from outside the function but keep their value between one execution of the function and the next.
- Variables created inside functions are local to the function and cease(停止) to exist when the function terminates.
- Some special arrays with their own rules:
- $GLOBALS: An array of all global variables.
- $_SERVER: An array of server environment variables.
- $_GET: An array of variables passed to the script via the GET method.
- $_POST: An array of variables passed to the scriptvia the POST method.
- $_COOKIE: An array of cookie variables
- $_FILES: An array of variables related to file uploads.
- $_ENV: An array of environment variables.
- $_REQUEST: An array of all user input including the contents of input including $_GET, $_POST, and $_COOKIE but not $_FILES.
- $_SESSION: An array of session(一段時間) variables.
6. Some Operators
6.1 Reference Operator
$a = 5;
$b = $a;
$a = 7;
$a = 5;
$b = &$a;
$a = 7;
6.2 Comparison Operators
0 == 0;
0 === 0;
6.3 Logical Operators
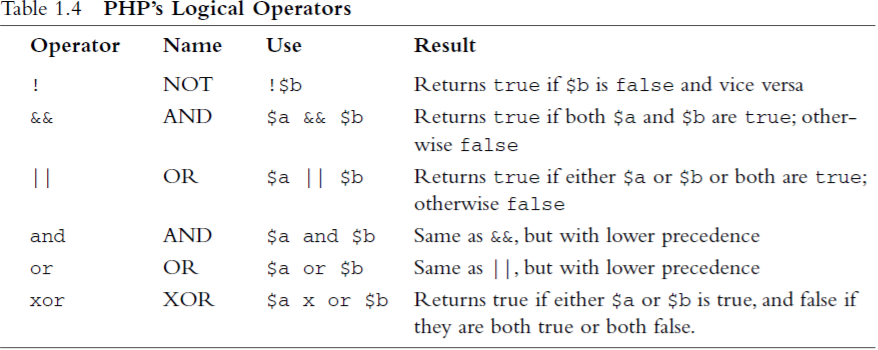
6.4 Bitwise Operators
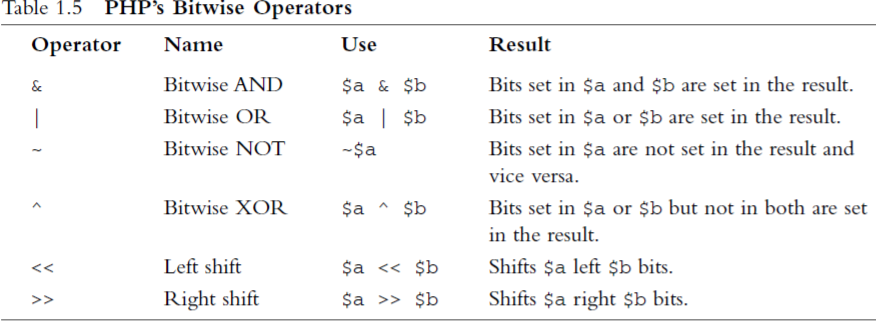
6.5 Array Operators
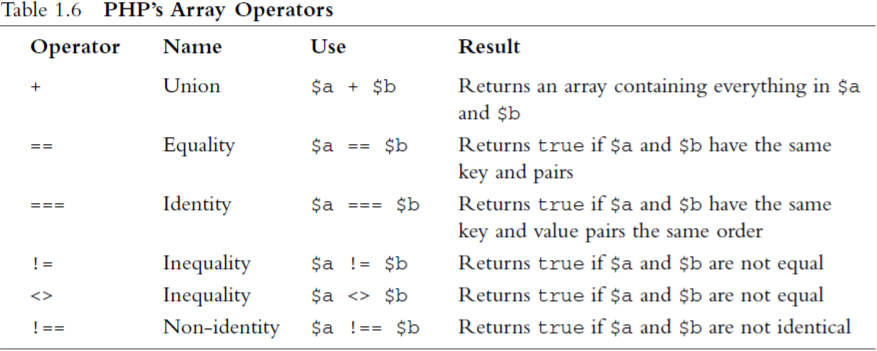
6.6 The Error Suppression Operator
- The error suppression operator (@) can be used in front of any expression to suppress(抑制) errors. (Those errors should be handled by error handling code)
- Error message can be stored in the global variable $php_errormsg when track_errors feature enabled in php.ini.
6.7 The Execution Operator
- a pair of backticks (``) is used to include executing commands.
$out = `ls -la`;
echo '<pre>' . $out . '</pre>';
6.8 Type Operators
class sampleClass{};
$myObject = new sampleClass();
if($myObject istanceof sampleClass)
echo("myObject is an instance of sampleClass");
7. Variable Functions
$a = 56;
echo(gettype($a) . '<br />');
settype($a, 'double');
echo(gettype($a) . '<br />');


